- A copay, short for copayment, is a fixed amount a healthcare beneficiary pays for covered medical services. The remaining balance is covered by the person's insurance company.
- The term health insurance co-pay is generally used interchangeably with co-insurance. The primary difference between co-pay and co-insurance is that under co-insurance, the insurer and the insured enter into an agreement where each party agrees to pay a percentage of the total cost.
- Copay Definition In Health Insurance
- Copay Meaning In Health Insurance Coverage
- Definition Health Insurance
Copay in Health Insurance refers to the percentage of the claim amount that has to be borne by the policyholder under a health insurance policy. Few insurance policies come with a mandatory clause for copayment, while others offer policyholders the option for voluntary copayment, which allows them to reduce their premium payment.
Posted on Jun, 2020Co-pay in health insurance refers to an arrangement between the insurance company and the insured. As per this agreement, policyholders have to pay a part of the medical expenses on their own, while the insurance company pays the remaining amount. Co-pay is applicable when you choose a health insurance policy with a co-pay clause. Here’s all you need to know about co-pay.
Why do insurance companies use the co-pay clause?
The co-pay clause is designed for the benefit of both the insurance provider and the insured. There are several legitimate reasons why many insurance companies include the co-pay clause in their health insurance policies. Listed below are some of them:
Copay Definition In Health Insurance

- The co-pay clause ensures that the insured party exercises judiciousness while filing a claim. Filing claims for unnecessary reasons can affect the premium payable when the policy is renewed. As such, the clause enables the insured to decide whether a claim is worth filing. By not filing an unnecessary insurance claim, the policyholder becomes eligible for discounts on premiums.
- The cost of treatment has been increasing with every passing year. If you decide to seek treatment in an expensive hospital, you may end up exhausting your sum assured. This in turn can increase your premium amount when you renew the policy. The co-pay clause ensures that policyholders do not compromise on treatment, but are, at the same time, mindful of the costs they would have to bear, for seeking expensive treatment.
- With the co-pay clause, the idea is to discourage wasteful expenditure for both the insured and the insurer. Since the co-pay clause requires policyholders to also contribute, they can determine whether it makes sense to opt for expensive healthcare as compared to quality healthcare.
- Co-pay affords a sense of awareness and ownership to the insured parties since they too have to bear a portion of the medical expenses.
Example to help understand co-pay
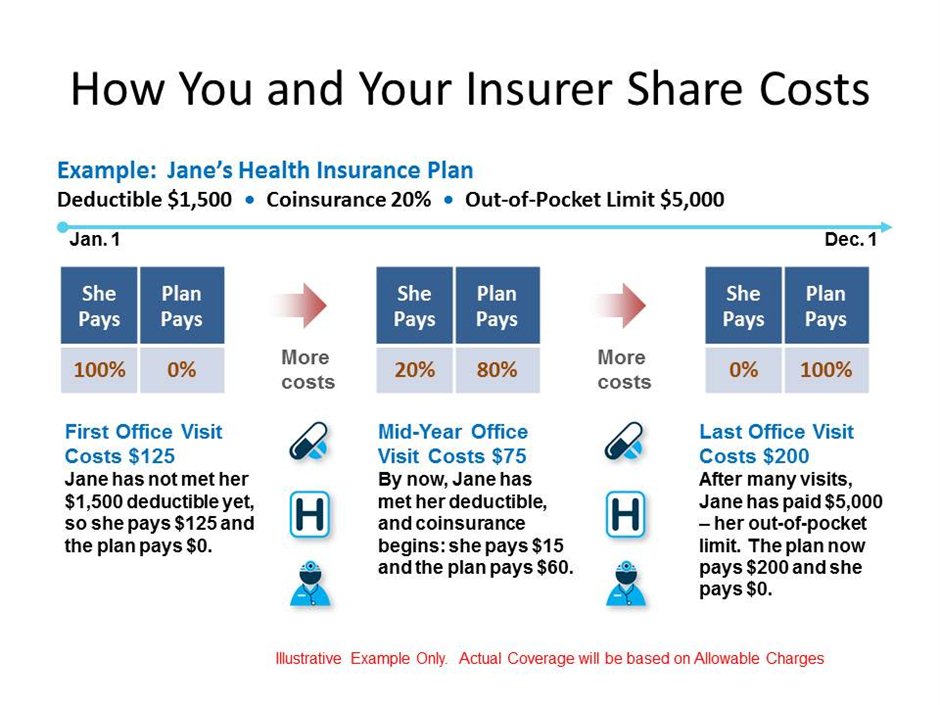
Let’s say your health insurance policy has a co-pay clause of 10%. Now, you have encashed your insurance policy, and the total medical expense amounts to ₹50,000. In such a case you need to pay 10%, i.e. ₹5,000 from your own pocket. Your insurance provider will bear the remaining amount of ₹45,000.
Features of co-payment
Before you decide to choose a policy with the co-pay clause, you need to understand its various features and how they would be applicable to you. Here are the general features
- Only a small, partial amount has to be paid by the policyholder. The insurance company will pay for the rest
- Co-pay clause applies to medical services, including hospitalization, doctor’s fees, lab tests, cost of medicines, etc.
- Health insurance plans with a higher premium amount generally have a lower co-payment percentage
- The main objective of the co-pay clause in health insurance is to save costs and discourage unnecessary claims
- Co-pay is mostly applicable to health insurance policies for senior citizens
Difference between co-pay and deductible
Most people seem to confuse co-pay with deductibles. Co-pay simply means that you must pay a specified, pre-determined portion or percentage of the medical expenses. On the other hand, the deductible is the amount you pay before the insurance provider pays for the costs incurred. Essentially, insurance providers are liable to pay the amounts exceeding the deductible. For instance, if the deductible is ₹25,000 and you file a claim of ₹60,000, the insurer is liable to pay only ₹35,000.
How to choose the right health insurance with co-pay?
Apart from knowing what a co-pay clause does, there are some other essential things you need to know to choose the right health insurance policy
Copay Meaning In Health Insurance Coverage
Co-pay percentage
The co-pay percentage is the cost that the policyholder will have to pay from the total medical bill. Before buying a health insurance policy with a co-pay clause, ensure that you check and understand the co-pay percentage as this will be the amount you pay from your pocket.
Premiums
Usually, policies with a co-pay clause have a lower premium as compared to other policies. As such, health plans with the co-pay clause can facilitate a lot of savings on insurance premiums.
Opting for co-pay – should you do it or not
Your health insurance policy covers you against more than just hospital bills. Apart from serving as a safety net in your hour of need, it covers you against several other expenses including doctor/surgeon fees, medical reports, and ambulance charges and so on. While choosing an insurance policy, you can decide whether or not to opt for the co-pay option. The answer to this is simple; people who are young and healthy and not suffering from any pre-existing diseases can benefit from opting for co-pay, as it can enable significant savings. With the co-pay clause, such people will not need to encash their entire insurance policy, while they can avail the many benefits that go with it.
Definition Health Insurance
While buying your insurance policy, reach out to us at Pinc Insurance to know more about the co-pay option. We provide in-depth insurance guidance, including assistance in purchasing policies and filing claims.




